A Key article to learn "Method of Tunneling in Soft Rock" providing easy access to learn
Classification of Method of tunneling in soft rock
1)Hard rock or fully self supporting
2)Soft soils requiring temporary support during and after construction.
Forepoling Method
Sequence of operation
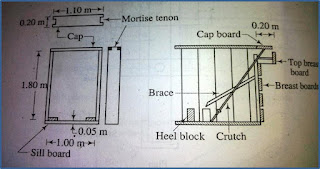
- The shaft is sunk from surface to the grade level and properly protected with timber sheeting
- A wooden bent properly braced is setup a few inches from sheeting
- Small holes at close interval are drilled through the sheeting to facilitate section being cutout.The pattern of holes are 3 inches apart above the cap and other lines of holes below the cap
- A peice of sheeting is cutout along the top lines of the holes
- Forepoles or spiles consists of planks with wedge end are entered one at a time and driven through cut,into the ground for half their lengths with an upward inclination of 2 inch per foot.
- After all the roof and part of side spiles are driven to half their length a timber is laid across the back ends of spiles and by wedging this down the front end of spiles are cantilevered up.
- A horse head is now set as a temporary support about 2 ft from sheeting.
- The next cap supported on a bridge is then set and temporarily supported on single post in method of tunnelling in soft rock
- Meanwhile side spiles are also driven for their full length
- The 18" breast board is now extended to grade level by adding new sheets.This new breast board act as a sheeting for next set of operation
Main points to be kept in mind in Method of tunneling in Soft Rock
- For running ground
- For laying sewer and gas pipe
- Splices inclined @ upward inclination of 170mm per metre
- 18" breast board used to extend grade level
- Horse head is used as temporary support
Needle beam Method
Sequence of operation
- The monkey drift for short distance of 3' is driven beyond days work
- The roof of the drift is supported by lagging carried on wodden segment which are in turn supported by two trench jack set in hitches cut in sides of monkey drift
- After this drift is completed the needle beam which is about 16' long is slowly skided forward into monkey drift
- The front end of needle beam rests on plank on floor of the drift while the rear end is carried on stout post resting on floor lining of the tunnel
- The outer trench jacks are removed and drift is widened sideways and supported as before by lagging and trench jack supported on sides of needle beam
- For firm ground in which roof stand for few minutes without support
- Monkey drift of 3 feet is provided beyond daywork
- Compressed air is provided for roof support @ pressure of 12lbs/sq
- It required large no. of trench jack
- Most suitable for Brick Lining
Army Method /Case Method
Main points to be kept in mind in Method of tunneling in soft Rock
- For constructing small c/s tunnel at fairly shallow depth
- For laying underground sewer
- Economical as only few jacks and planks required
American Method
Main points to be kept in mind Method of tunneling in soft rock
- For large size railway and highway tunnel
- 16 feet plate @ springing
- Heavy timber not required
- For large size tunnel
- Unsuitable for tunnel have flat bottom
English Method

English Method

Main points to be kept in mind in Method of tunneling in soft rock
- Load on roof supported by underpinning
- Central top heading of 16 feet is provided
- Cavity danger in unstable soil is main disadvantage
- Large use of timber and frequent shifting of timber is not economical
Belgian Method
Main points to be kept in mind in Method of tunneling in soft rock
- Used for moderately firm or hard soil
- For Light section of timber
- Due to Underpinning cause settlement is main disadvantage
- Method not adopted for depth greater than 1700m
German Method
Main points to be kept in mind in Method of tunneling in soft rock
- For supporting roof and side
- 3 drift are used one along crown and to along wall
- Heavy Strut not required
Conclusion:
This is full article regarding the Method of tunneling in soft rock which is mainly asked in exam and by this information you will be able to know more about the practical approach of this methods





Comments
Post a Comment