Understand the methodology with practical example for the topic Tunneling in Hard Rock
 |
Tunneling in hard rock is mostly an operation that has to be carried out at considerable depth below the natural ground surface, the work being carried out in hilly tracts. Such a tunnel has been constructed with an advantage for carrying railway, water, highway, and for diversion of water from one valley to another across the intervening ridge. Comparing to soft soil tunneling the operation is very costly.
Rock is a material which is self-supporting and does not require much timbering except occasionally in regions where loose rock is met with. It admits of operation in many sections along the length of the tunnel which greatly helps to expedite the work
Faces of operation for Tunneling in hard rock
These faces of operation are opened up by :
- System of vertical shaft
- System of pilot tunneling
1)System of vertical shaft
On the tunnel line at suitable points shafts are sunk and if n is the no. of shaft that are possible 2n + 2 faces of attack are available
2)System of pilot tunnel
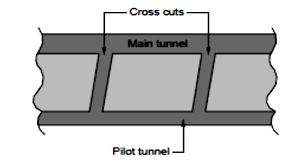
It is found that lateral or horizontal approach to the tunnel line may be closer and shorter compared to deep vertical shaft.In such a case a tunnel of small size called a pilot tunnel is driven parallel and closed to the proposed main tunnel and short cross connecting tunnels are driven from it to reach the proposed main tunnel to create operational faces
 |
| Pilot tunnel |
Methods of Tunneling in Hard Rocks
Th popular methods are:
- Drift Method
- Heading and bench method
- Full face method
- Pilot tunnel method
DRIFT METHOD
Points to be kept in mind
1)Suitable for large size tunnel in competent rock
2)Small tunnel upto 300mm×300mm can be made
3)Enlarging and benching work commences but for mucking there is frequent shifting of drift from bench to bench is main disadvantage
4)Small preliminary section for full length can be driven accurately and it elaborate supporting platform
 |
| Drift |
a)Boring or blasting top centre heading or drift end to end
b)Widening and enlarging the drift
c)Benching in stages
TYPES OF DRIFT
1)Central drift method : Time consuming,good ventilation,eliminates supporting platform
2)Side drift method:Used for tunneling work of large cross section
3)Bottom drift method:Are of low height roof can be properly lined and platform avoided
4)Top drift method : for smaller section and most popular section
 |
| Types of Drift |
Heading and Benching Method
Points to be kept in mind
- Involve driving of portion in advance of bottom portion
- Can excavate full width of tunnel above spraining level
- Less quantity of explosive required as compare to full face method
- Useful when tunnel section is large
- For railway tunnel
- Heading benching and mucking can be done simultaneously
Full Face Method
Points to be kept in mind
- For tunnel of small c/s through stable and self supporting rocks
- This is continuous method
- Tunnel upto 10 ft is handled properly
- For small c/s area diameter less than 6m and face area less than 19 m2length not more than 3m
- For large size tunnel popular size of hole vary from 10mm to 40mm & holes are drill are spacing of 120mm c/c
- This section minimize settlement
Pilot Tunnel Method
- Tunnel c/s area -240*240 m2
- It is also used for storing tools and material during construction method
- Used for removing muck from tunnel for proper ventilation


Comments
Post a Comment